



If you’ve been shopping around for china aluminum parts machining, you’ve probably noticed two things: lead times are tightening, and expectations are rising. That’s the paradox. Automation has made tolerances tighter, yet real-world buyers still want flexibility, fair MOQs, and straightforward quality gates. I’ve toured more than a dozen plants; some over-promise. A few deliver consistently.

Across EV platforms, robotics, and machinery, buyers keep asking for thinner walls (≈1.5–2.0 mm), fewer secondary ops, and traceability that doesn’t slow production. To be honest, sustainability is no longer a “nice-to-have”: recycled alloy content and energy monitoring are being written into RFQs. Many customers say they’ll pay a small premium for verified porosity control and consistent anodizing color. I guess that’s the new normal.
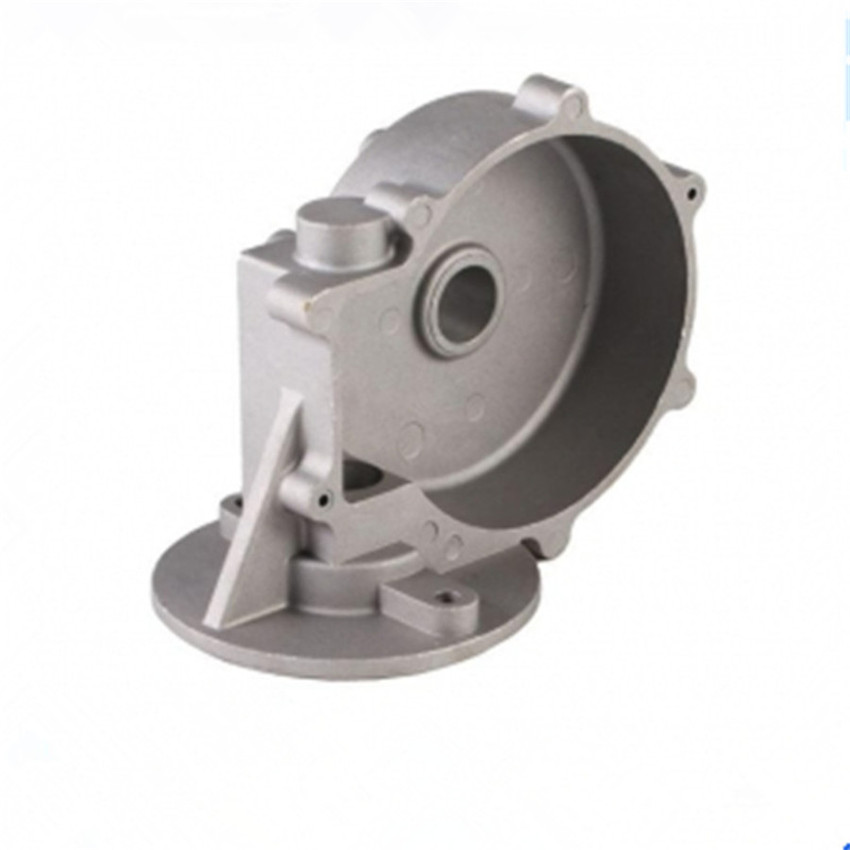

Origin: Gelan Building, No.256 Xisanzhuang Street, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China. Short Description: Basic Info — Die Casting Machine Type: Cold Chamber; Die Casting Method: Precision; Application: Machinery Parts; Machining: CNC Machining; Material: Aluminum; Surface Preparation: Polishing; Pressure Chamber: Vertical; Tolerance Grade: 8.
| Parameter | Specification (real-world use may vary) |
|---|---|
| Process | Cold-chamber precision die casting + CNC machining (3/4/5-axis) |
| Alloys | ADC12/A380 (die cast), 6061-T6 (machined ops), others on request |
| Tolerance | Grade 8 (≈ IT8/CT8); typical ±0.05–0.10 mm on criticals after CNC |
| Wall thickness | ≈1.5–3.5 mm, geometry-dependent |
| Surface | Polishing standard; anodizing, powder coat, chromate optional |
| QA & Testing | CMM, X-ray porosity, tensile per ASTM E8/E8M, salt spray 120–480 h |
| Tool/die life | ≈80k–120k shots (alloy and maintenance dependent) |
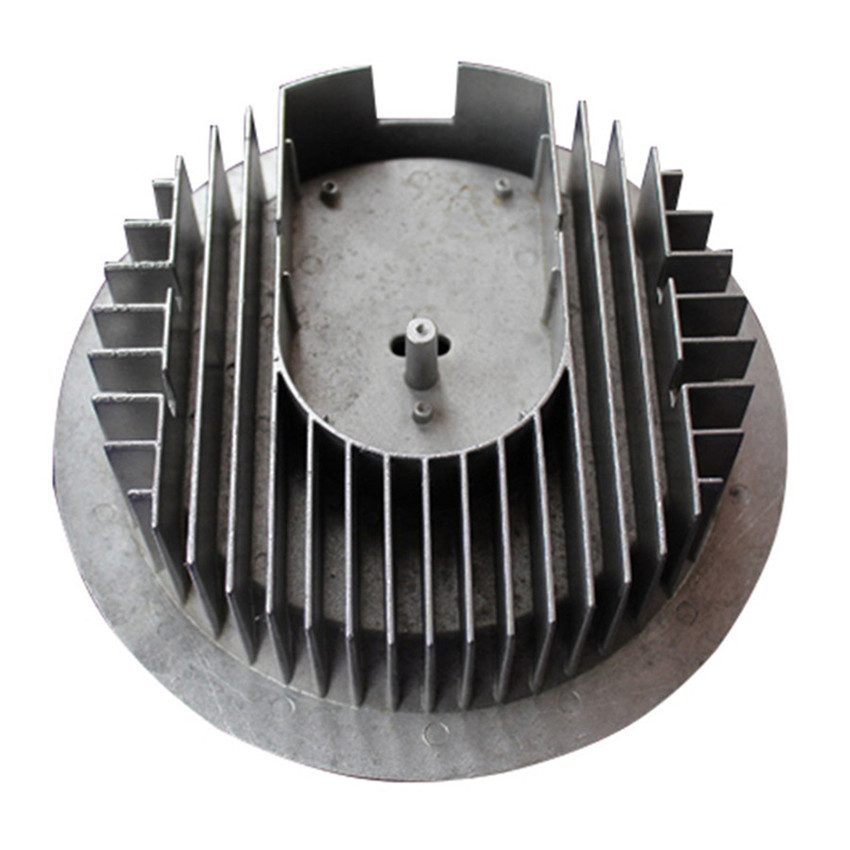

Applications: machinery housings, robot gearcase covers, small EV motor brackets, UAV gimbals. Typical service life in the field? Around 5–10 years, depending on load cycles, coating, and environment.
| Vendor | Certs | Typical tolerance | Lead time | MOQ | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mingda Metals | ISO 9001, IATF 16949 (stated) | ±0.05–0.10 mm after CNC | Tooling 3–5 wks; mass prod 2–4 wks | ≈500 pcs | X-ray per lot; PPAP/FAI on request |
| Coastal Supplier B | ISO 9001 | ±0.08–0.15 mm | 4–6 wks | 1,000 pcs | Limited moldflow |
| Boutique Shop C | ISO 9001 (pending) | ±0.05 mm (low volume) | 6–8 wks | ≈100 pcs | Good prototyping; pricier |
Customization includes DFM, draft-angle optimization, thread inserts, and mixed finishing. One robotics customer told me, “Cycle time dropped 14% after gate redesign.” Another buyer noted more consistent flatness (0.1 mm/100 mm) after switching to china aluminum parts machining with X-ray gated control.
Case 1: an EV accessory maker moved from sand cast + mill to die casting + minor CNC; unit cost fell ≈19% and yield improved to 98.3%. Case 2: a drone brand demanded ΔE ≤ 2 anodize; after pre-anodize etch tuning, reject rate dropped under 1.5%—surprisingly fast win.
Look for ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 when automotive traceability is in play. Dimensional checks aligned with ISO 2768; casting per GB/T 9438 or EN 1706; tensile per ASTM E8/E8M. For many buyers, that’s the difference between smooth PPAP and a month of firefighting. If your RFQ references china aluminum parts machining, spell out porosity class, salt spray hours, and critical datum callouts—vendors appreciate clarity.
Authoritative citations: